Frequently asked questions
It is also possible to speak to someone directly.
Electric Vehicles
Sustainability EVs contribute to better air quality due to lower CO2 emissions then petrol or diesel cars. Changing onw means you are ahead of the curve. Modern Technology- the latest generation of EVs has a realistic range of up to 500km on a charge, with more charging stations being added. Charging an electric car costs less than filling a petrol or diesel tank.
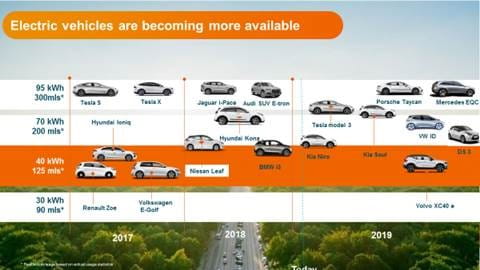
More EV's available each year EVs are becoming more accessible and affordable, thanks to rapidly developing innovations in companies such as Tesla, but also established car brands such as Audi, BMW, Mercedes, Volkswagen and Nissan. Charging infrastructure and technology is also continuously developing and improving in recent years.
Upcoming legislation changes To accelerate the EV resolution, new legislation around electric vehicles were introduced. In June 2022, a European Parliament vote mandated that all the new cars and vans sold in the European Union should be zero-emission vehicles by 2036. Manufacturers will no longer be allowed to sell new cars or LCV's with an internal combustion engines. In 2030, the EU will aim to have at least 30 million electric vehicles on the roads. More and more cities are implementing low-emission zones (LEZs) as they look to improve air quality.
Benefits for fleets Since EV's don't produce any direct emissions, companies can make considerable progress towards their sustainability goals by shifting to an EV fleet. The improved efficiency of EVs will only become more attractive for fleet managers in the years to come. What's more, maintenance costs for EV's are considerably lower. And, also important to mention, to meet the growing number of EV's on the road the EV charging infrastructure is growing rapidly.
A full electric vehicle, also called an EV, only uses a battery and a motor to drive the engine. It is powered by a battery that you charge via a charging point (whether this is at home, the workplace or a public access point).
This depends on the battery size and efficiency of the vehicle. Generally speaking, you can drive 125 to 150 miles on a fully charged 40 kWh battery. However, if you drive sensibly, you can go even further. Vehicles with a 64-kWh battery have a range of 200 to 250 miles.
Speed is the biggest drain on the battery, so it’s worth keeping to speed limits. Other factors that can influence your driving range include:
- High or low temperatures (as you may be using the air conditioning/heating more)
- Driving into a strong headwind
- A fully loaded vehicle
- Driving uphill for a long period of time
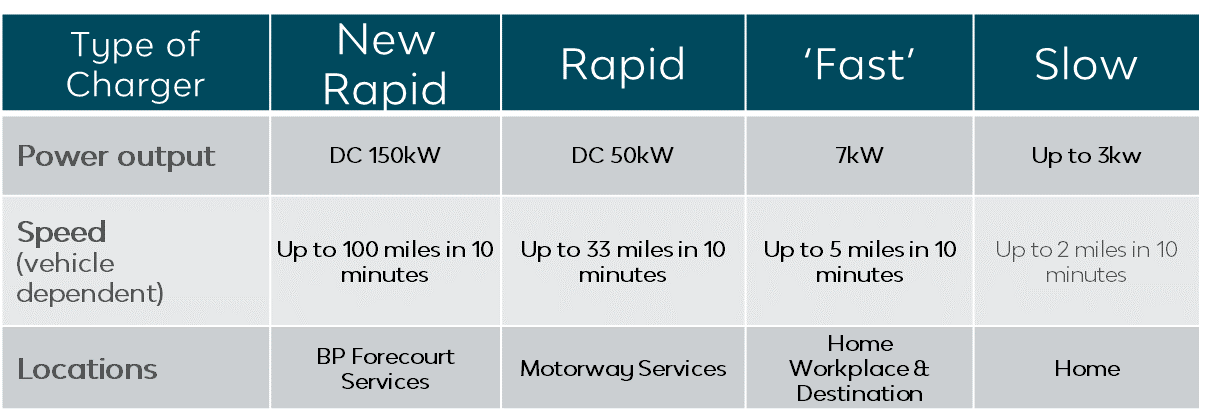
There are several different types of charging options available in the UK. Rapid DC points use tethered cables, which are attached to charging unit. It is important that you know what types of charge-point your vehicle can use.
If you are charging a car with a domestic three-pin power socket or 3kw charger, it will take around 12 hours. With a 7kW fast charger (such as home/public chargers) it takes around three to four hours. If you use the rapid AC/DC charges found at motorway services, your battery will be 80% charged in approximately 30 minutes (though you need to remember that fast chargers are more expensive than standard charging stations).
Types of charge-points include:
It needs less maintenance, as the engine has fewer moving parts and no exhaust or gears. You also won’t need to change the oil and the brakes should wear less thanks to regenerative braking.
The automotive industry is heavily regulated, ensuring all products are safe. Beyond statutory standards of electric car safety there are Euro NCAP ratings, providing an “out of 5 star” rating. Like conventional vehicles, in the event of a collision, there is a small chance that a vehicle part may receive an active charge, or that short-circuiting could cause an electrical fire, but safety precautions and construction in addition to the statutory standards, as outlined above have limited this risk to an absolute minimum.
Yes. They are a similar to driving with automatic transmission and in some cases, even simpler. You just choose drive or reverse, as with an automatic, but you don’t have to brake as often. This is thanks to the regenerative braking system that slows down the car when you take your foot off the accelerator.
The equipment is the same for comfort, safety and technology. Electric vehicles may also have added features to help you manage your journey, such as a connected navigation system showing charge points or a smartphone application to control your charge from your phone.
We already offer quite a few electric vehicles and there are many more on the way. Our current range features: